Indian Space Research Institute (ISRO) on 27th November successfully launched Advanced Remote Sensing Satellite CARTOSAT-3 from Sriharikota in Andhra Pradesh. This is ISRO’s fifth mission of the year. Along with Cartosat, 13 small Nanosatellites from the US were also placed in their orbits. This launch was done with the PSLV-C47 rocket. CARTOSAT-3 will be used to gather weather and courteous information. With this, India has completed the figure of launching more than 300 foreign satellites.
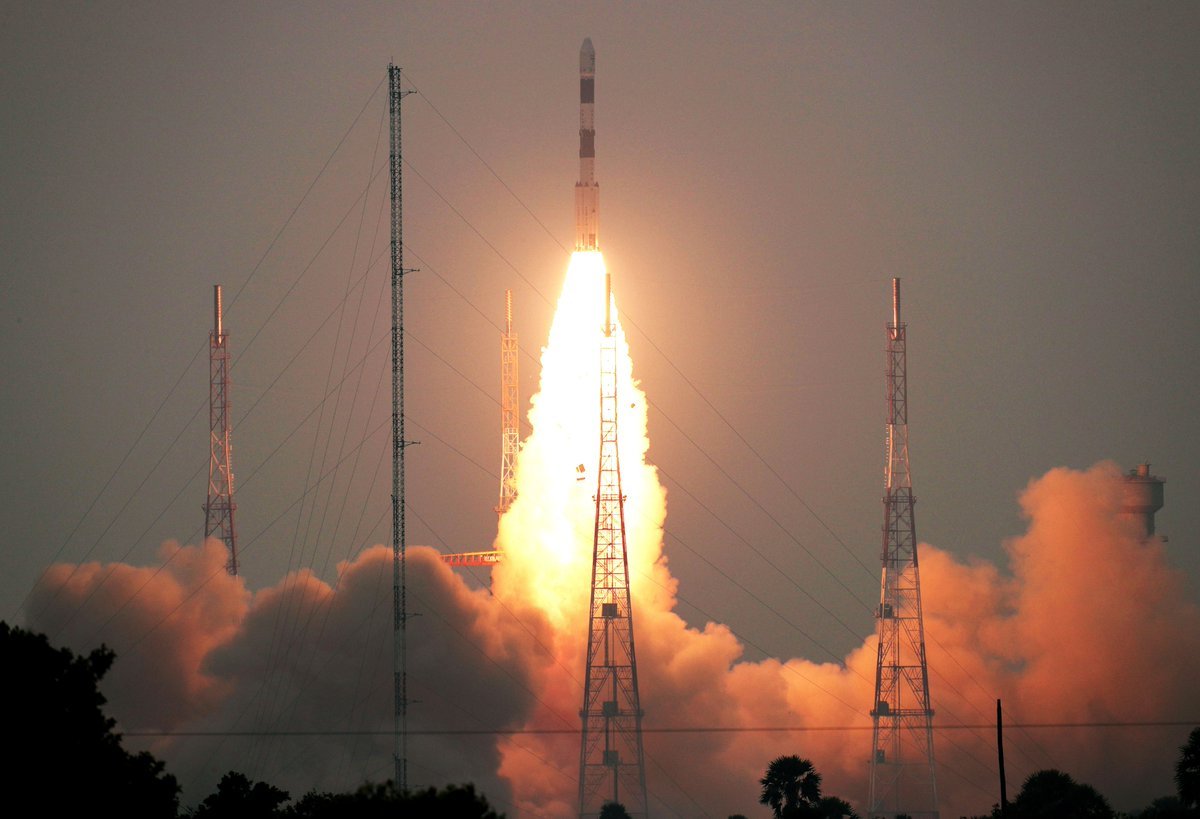

Following the successful launch of the satellite, ISRO chief K Sivan said, “I am delighted that the PSLV C-47 successfully orbited 13 satellites with CARTOSAT-3. It is a high-resolution civilian satellite. We have 13 missions in the queue till 6 March. These include 6 large vehicle missions, while 7 are satellite missions. ”
Why is CARTOSAT-3 Beneficial For India?

CARTOSAT-3 weighs around 1500 kg. It is the first of the third generation advanced high-resolution Earth-imaging satellites. The Indian space agency has been launching remote sensing satellites since 1988. Through these satellites, ISRO gets high-resolution images of the Earth. They are used for 3-D mapping, disaster management, agriculture planning, water management, and border security. It is being called India’s Eye on Sky. There are some special reasons for this and is the 9th satellite of the CARTOSAT series.
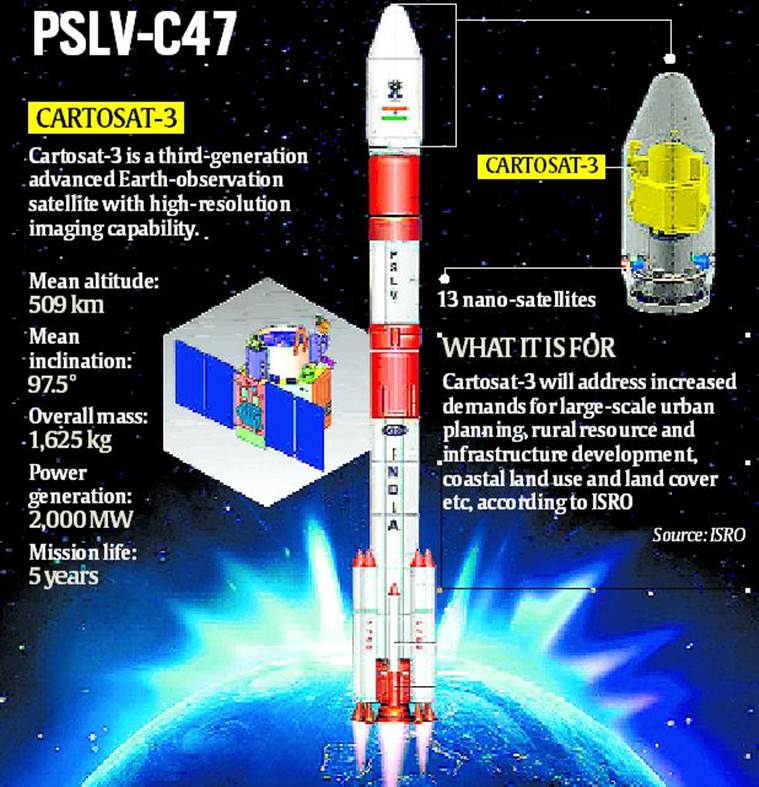
In addition to the high-resolution Spatial Camera installed in CARTOSAT 3, it will be able to take very clear pictures from a height of about 509 km from the earth. This satellite is the most advanced type of observatory satellite that India has so far launched. One can also see its Advanced Spatial Resolution in such a way that even a one-foot object on the ground can be easily identified with the help of this satellite.

It will also play an important role in India’s security in the future. It will also be beneficial for security forces in many ways as the Space Surveillance will be increased. This is the first satellite that can cover a Spatial Range of 16 km distance in Panchromatic Mode. Apart from this, it can also easily capture multi-spectrum and hyperspectral.









